LibSPN: A Library for Learning and Inference with Sum-Product Networks and TensorFlow
LIBSPN is a general-purpose Python library for building, learning, and performing exact inference in Sum-Product Networks (SPNs) at scale, tightly integrated with TensorFlow (plus custom C++/CUDA ops) to enable efficient CPU/GPU execution, structure manipulation, and practical end-to-end workflows.
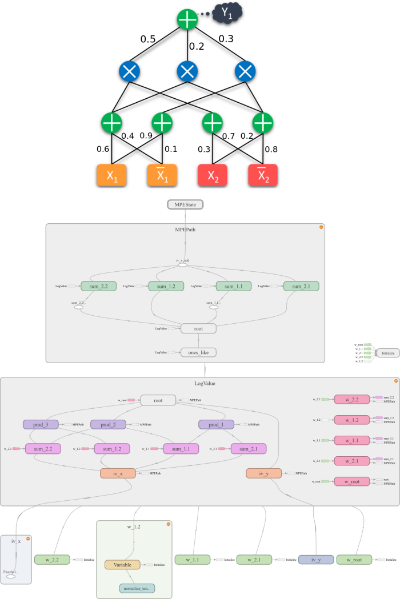
Overview
Sum-Product Networks (SPNs) are a probabilistic deep architecture with solid theoretical foundations, which demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in several domains. Yet, surprisingly, there are no mature, general-purpose SPN implementations that would serve as a platform for the community of machine learning researchers centered around SPNs. Here, we present a new general-purpose Python library called LIBSPN, which aims to become such a platform. The library is designed to make it straightforward and effortless to apply various SPN architectures to large-scale datasets and problems. The library achieves scalability and efficiency, thanks to a tight coupling with TensorFlow, a framework already used by a large community of researchers and developers in multiple domains. We describe the design and benefits of L IB SPN, give several use-case examples, and demonstrate the applicability of the library to real-world problems on the example of spatial understanding in mobile robotics.
Features
- Introduces LIBSPN, an actively maintained, domain-independent SPN library designed to be a shared platform for SPN research and applications.
- Defines a dynamic SPN graph abstraction (variables/ops/parameters) that supports automatic validity checking, scope calculation, structure generation, and pruning beyond TensorFlow’s static graphs.
- Achieves scalable CPU/GPU execution via tight TensorFlow coupling and custom SPN-specific TensorFlow ops implemented in C++/CUDA for efficiency.
- Provides a broad toolbox for learning and inference (e.g., batch/online learning, hard EM, marginal + MPE inference, explicit latent variables, weight sharing, save/load, visualization, CLI).
- Demonstrates real-world applicability on robot spatial understanding, outperforming SVM baselines on classification/novelty detection and showing strong generative capabilities (completion + prototypes) with real-time inference.
Publication
A. Pronobis, A. Ranganath, and R.P. Rao, "LibSPN: A Library for Learning and Inference with Sum-Product Networks and TensorFlow", in Workshop on Principled Approaches to Deep Learning, ICML 2017, Sydney, Australia, Aug 2017.
Download PDF